JDBC 이해
JDBC의 등장 이유
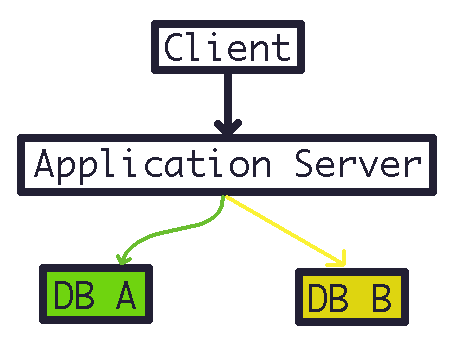
- 대부분의 서비스는 위의 그림과 같이 데이터를 DB에 저장한다.
- 애플리케이션이 DB에 접근하는 과정은 다음과 같다.
- 커넥션 연결
- SQL 전송
- 응답 결과 수신
- DB의 종류는 여러 가지가 있고, 각각의 DB마다 통신하는 방식이 다 다르다.
- DB를 다른 종류로 변경하면, DB에 접근하는데 사용했던 코드들이 다 바뀌어야 한다.
- 개발자가 다른 종류의 DB 통신 방법을 새로 학습해야 한다.
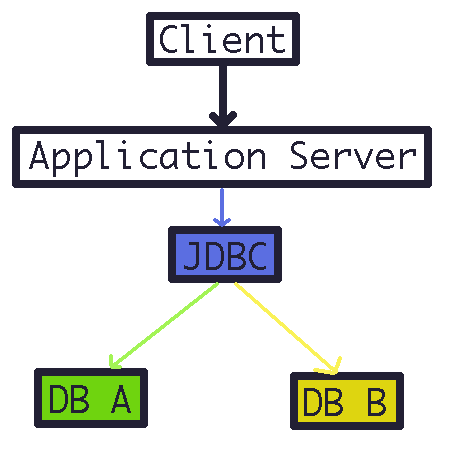
- JDBC는 이러한 문제들을 해결하기 위해 만들어졌다.
- JDBC는 DB 접근에 관한 표준 인터페이스를 제공한다.
- 커넥션 연결 : java.sql.Connection
- SQL 전송 : java.sql.Statement
- 응답 결과 수신 : java.sql.ResultSet
- 각각의 DB에 맞는 드라이버만 사용하면, 코드의 변경 없이 DB를 바꾸는 것이 가능해졌다.
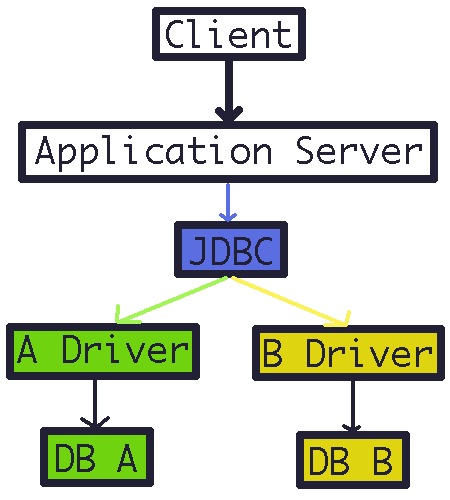 Driver를 사용해 각각 다른 통신 방식을 JDBC로 통합
Driver를 사용해 각각 다른 통신 방식을 JDBC로 통합
- DB를 다른 종류로 변경하면, DB에 접근하는데 사용했던 코드들이 다 바뀌어야 한다.
- 사용자 코드에는 JDBC 코드만 들어가게 된다.
- DB가 변경되어도 Driver만 바꿔주면 된다.
- 개발자가 다른 종류의 DB 통신 방법을 새로 학습해야 한다.
- JDBC 코드만 잘 사용할줄 알면 된다.
하지만 ANSI SQL 외에 다른 SQL은 DB마다 다른 점이 있다. DB가 변경되었을 때 JDBC 사용 코드는 변하지 않겠지만, DB에 맞게 SQL문을 다시 작성해야 할 수도 있다.
JDBC DriverManager
- JDBC는 필요한 Driver를 어떻게 찾아오는 걸까?
- 그 역할을 하는게 JDBC DriverManager이다.
- DriverManager는 사용 가능한 Driver를 찾아내고, 데이터베이스 와의 적절한 연결 설정을 처리한다.
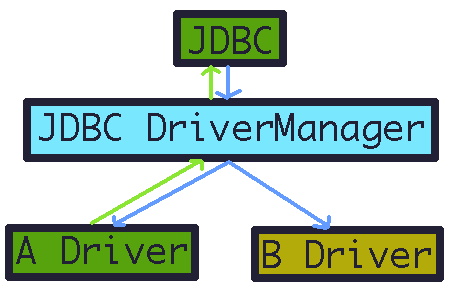 DriverManager가 적절한 드라이버 커넥션을 찾아다 준다
DriverManager가 적절한 드라이버 커넥션을 찾아다 준다
- JDBC DriverManager는 등록된 라이브러리의 이름을 통해 Driver 클래스들을 만들어 갖고 있는다.
- Driver를 찾을 수 없다면, ClassNotFoundException을 날린다.
- 사용자가 JDBC 인터페이스를 통해 커넥션을 요구한다.
- Driver 클래스들에게 커넥션을 요청한다.
- 각 Driver들은 본인이 처리할 수 있는 요청일 경우 커넥션을 반환한다.
- 본인이 처리할 수 없다면, 다음 순서에게 요청이 넘어간다.
- 적절한 커넥션이 사용자에게 전달된다.
JDBC의 사용
JDBC를 이용해 간단한 crud 코드를 작성해본다.
- Connection, Statement, ResultSet 같은 모든 자원들은 꼭 역순으로 close() 해줘야 한다.
Create
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public void create(Book book) {
String sql = "insert into book(id, title) values(?, ?)";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.preparedStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setLong(1, book.getId());
preparedStatement.setString(2, book.getTitle());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 1 : row 개수 나옴
} catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Read
findById
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public Book findById(Long bookId) {
String sql = "select * from book where id=?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.preparedStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setLong(bookId);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()) {
Long id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String title = resultSet.getString("title");
Book foundBook = new Book(id, title);
return foundBook;
}
} catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
findAll
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public List<Book> findAll() {
List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
String sql = "select * from book";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.preparedStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while(resultSet.next()) {
Long id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String title = resultSet.getString("title");
Book foundBook = new Book(id, title);
bookList.add(foundBook);
}
return bookList;
} catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Update
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public void update(Long bookId, String title) {
String sql = "update book set title=? where id=?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.preparedStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, title);
preparedStatement.setLong(2, bookId);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Delete
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public void create(Long bookId) {
String sql = "delete from book where id=?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.preparedStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setLong(1, bookId);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.